
DOING HOLDINGS

DOING HOLDINGS
Pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process that occurs in the absence of oxygen or any other reactive gases.
The primary reason oxygen is not required (and is actually avoided) in pyrolysis is to prevent combustion or oxidation reactions. Here's why:
When oxygen is present, waste tire, plastic, rubber or organic materials can combust, leading to the release of energy in the form of heat and light. This combustion process produces carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O) as primary byproducts, which is not the goal of pyrolysis. Pyrolysis aims to break down materials into smaller molecules, such as gases, liquids (pyrolysis oil/HFO heavy fuel oil/WDF waste derived fuel), and carbon black, without burning them. For instance, in the case of waste tire pyrolysis, the presence of oxygen would lead to rapid combustion of the tires, causing a sharp increase in temperature. This could damage the pyrolysis machine and generate harmful gases like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, severely polluting the environment. In contrast, oxygen-free pyrolysis allows waste tires to decompose gradually at a relatively lower and controllable temperature, producing high value products such as carbon black, steel wire, and fuel oil.
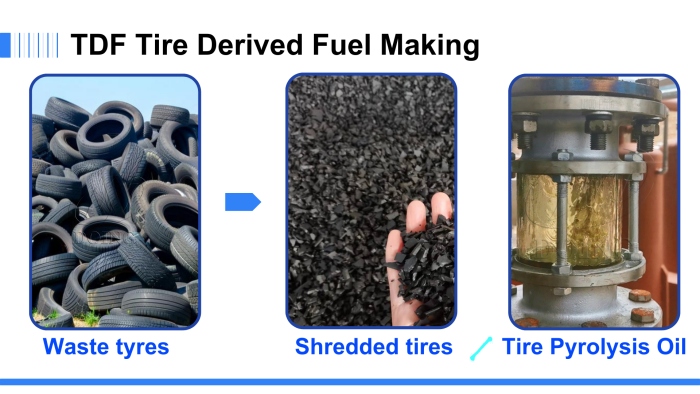
Waste tire pyrolysis product
Pyrolysis relies on heat to break chemical bonds in the absence of oxygen, leading to the decomposition of organic materials into simpler compounds. This controlled pyrolysis process allows for the production of valuable byproducts like syngas (a mixture of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and other gases), pyrolysis oil, and carbon black, which can be used for energy, chemicals, or soil amendment. Unlike combustion, which is a rapid and uncontrolled reaction, pyrolysis occurs in a carefully regulated environment. By precisely controlling parameters such as temperature, heating rate, and residence time, the decomposition process can be optimized to maximize the yield and quality of the desired products.
Oxygen can react with the organic material, leading to oxidation reactions that alter the chemical composition of the products. By excluding oxygen, pyrolysis ensures that the the process occurs through non-oxidative pathways, preserving the desired chemical properties of the output. Oxidation reactions often result in the formation of oxygen-containing compounds such as carboxylic acids, ketones, and aldehydes, which may not be suitable for the intended applications of the pyrolysis products. In oxygen-free pyrolysis, the absence of oxygen prevents these unwanted oxidation reactions.
Pyrolysis is designed to be an energy-efficient process that maximizes the yield of useful products. Introducing oxygen would lead to partial combustion, reducing the efficiency and yield of the desired products.Combustion consumes part of the organic material to produce heat, which can lower the overall energy efficiency of the process. In contrast, oxygen-free pyrolysis minimizes energy losses by focusing the thermal energy on breaking chemical bonds rather than sustaining combustion. This results in a higher yield of valuable products. For example, in the pyrolysis of waste plastics, an oxygen-free environment allows for a more efficient conversion of the plastic into syngas and pyrolysis oil, which can be further refined into transportation fuels or used as feedstocks for the chemical industry.

Applications of waste oil to diesel
Compared to traditional waste treatment methods like combustion, oxygen-free pyrolysis offers several advantages. Combustion, while capable of handling large amounts of waste and generating electricity, produces fly ash and dioxins that are difficult and costly to treat. Additionally, the emissions from combustion may contain harmful pollutants that require stringent control measures. On the other hand, oxygen-free pyrolysis generates cleaner gases and liquids, and the solid residues can be recycled, achieving a more environmentally friendly conversion of waste. For example, the carbon black produced from pyrolysis can be used in the manufacturing of tires and other rubber products, while the pyrolysis oil can be refined into diesel or gasoline, providing a sustainable alternative to conventional fossil fuels.

Final products and applications from waste plastic pyrolysis plant
In summary, pyrolysis does not require oxygen because its goal is to thermally decompose materials in a controlled environment to produce specific chemical products, rather than burning them. The absence of oxygen ensures that the process remains non-combustive and maximizes the yield of valuable byproducts.
DOING waste pyrolysis and oil refinery plants manufacturer
If you want to learn more about pyrolysis, or if you want to learn about pyrolysis machine, please contact us. Our DOING Company, as a professional manufacturer of pyrolysis machine, offers comprehensive services including equipment design, installation, and after-sales support. We are dedicated to providing customized solutions for waste treatment, helping customers achieve efficient waste recycling. Our expertise and commitment to quality ensure that our clients can fully benefit from the advantages of oxygen-free pyrolysis technology.